macOS employs multiple security layers to defend against malware, ensuring your device stays secure without hampering performance. This article explains core security features, how they work together, and practical steps users can take to enhance macOS malware protection.
Gatekeeper: macOS’s Core Security Mechanism
Gatekeeper plays a key role in macOS security by verifying app authenticity, blocking unauthorized software, and providing layered protection through Apple’s ecosystem. This feature ensures that applications come from trusted sources, reducing risks from third-party software.
Key Protection Strategies
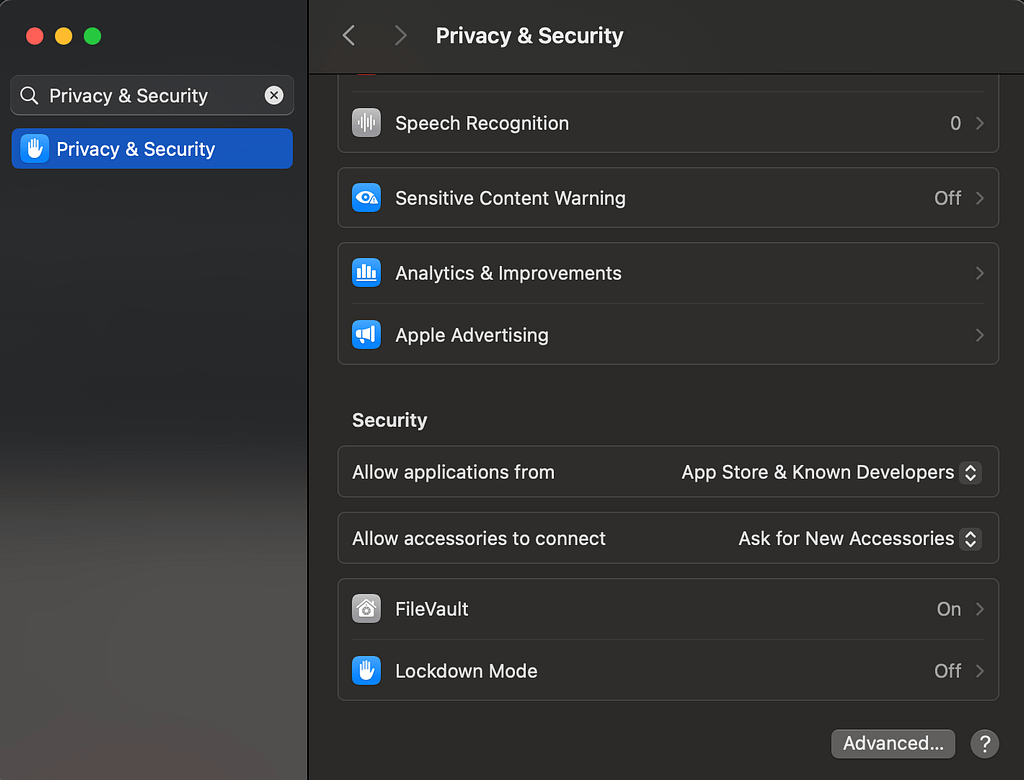
- App Verification: Gatekeeper checks app authenticity before they can run, confirming they are from identified developers and are notarized by Apple.
- Code Signing Checks: App files must be digitally signed using a Developer ID certificate. This process detects any file modifications since signing and blocks potentially compromised applications.
- Notarization: Apps downloaded outside the App Store undergo notarization, a scanning process that verifies safety. Notarization offers additional protection against malicious software that is detected after release.
User-Controlled Security Options
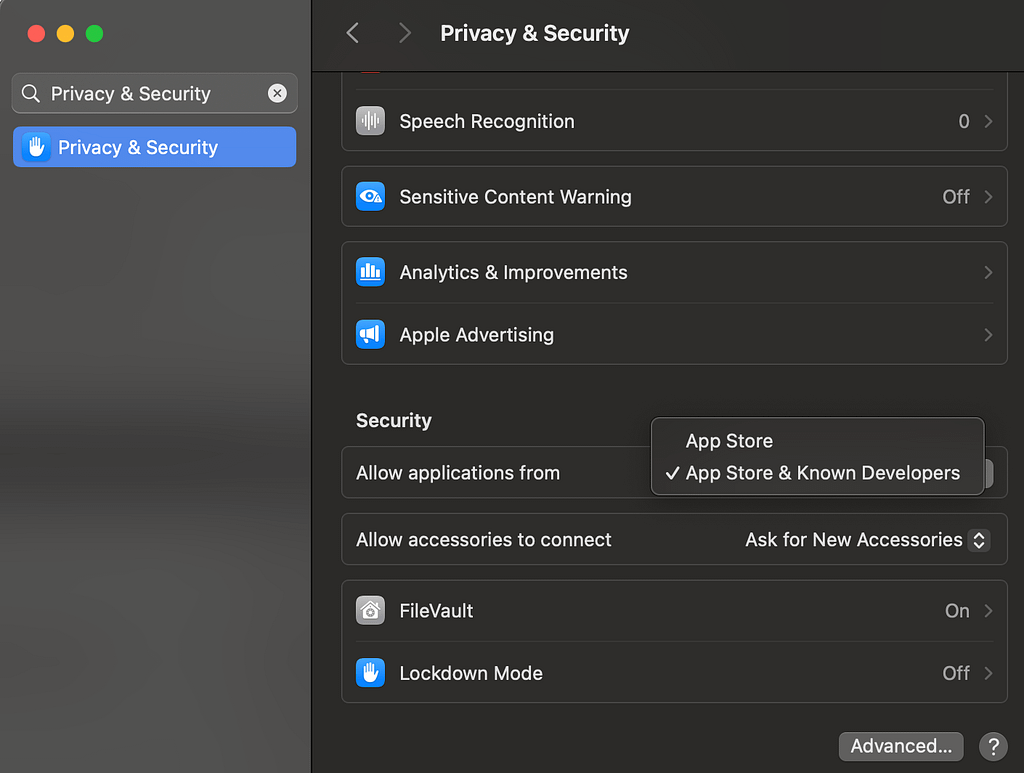
macOS offers flexible Gatekeeper options, allowing users to choose the desired security level:
| Security Level | Description |
|---|---|
| App Store Only | Restricts app downloads to only App Store sources |
| App Store + Identified Developers | Allows Apple-verified apps from third-party developers |
| Full Control | Permits overriding Gatekeeper protections (not advised) |
Tip: Combine Gatekeeper with System Integrity Protection (SIP) for a multi-layered defense against unauthorized access and modifications.
Built-in Security Layers
macOS’s defense system integrates several protective layers, each designed to target different threat levels. These include preventive measures, active malware detection, and advanced protection mechanisms that ensure user and system safety.
1. Preventive Measures
App Store Verification
Apple screens all apps in the App Store to verify they meet stringent safety and quality standards, ensuring they are free from known threats.
Gatekeeper & Notarization
Gatekeeper and notarization protocols work in tandem to block unsigned software and require verification before running any app not from the App Store. This minimizes exposure to risky downloads.
2. Malware Detection: XProtect
XProtect, macOS’s built-in antivirus tool, leverages YARA signatures to detect and block known malware:
- Automatic Scans: XProtect scans apps upon first launch, proactively identifying threats before they can impact your system.
- Real-Time Blocking: When a potentially harmful file is detected, XProtect prevents it from opening and notifies users of the risk.
3. Advanced Protection Features
| Feature | Protection Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Sandboxing | Isolates apps from system components and other applications |
| System Integrity Protection (SIP) | Restricts root user modifications to core system processes |
| Transparency, Consent, and Control (TCC) | Manages permissions for apps accessing sensitive data |
Sandboxing and SIP add significant security, restricting apps’ access to the system and minimizing vulnerabilities from unauthorized software.
Quick Note: TCC settings help protect user data by requiring consent for app permissions, safeguarding personal information from unauthorized access.
Additional macOS Security Features
macOS includes several additional features to bolster user protection:
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized network traffic |
| FileVault | Encrypts disk storage for enhanced data security |
| Password Monitoring | Alerts users of leaked credentials |
These features reinforce macOS’s defensive architecture, ensuring that data remains secure even if the device is lost or exposed to potential threats.
Best Practices for Maximizing macOS Security
Enhance your device’s security by following these practical tips:
- Download Apps Only from Trusted Sources: Stick to the Mac App Store or apps verified by Gatekeeper to minimize exposure to malware.
- Keep macOS Updated: Regular updates address vulnerabilities, ensuring your system remains resilient against new threats.
- Enable Built-in Security Features: Utilize macOS’s firewall, FileVault, and SIP for comprehensive protection.
- Consider Third-Party Antivirus Software: While macOS has strong defenses, additional antivirus software can offer layered protection.
Important: While macOS is designed with robust security, cautious usage and keeping your software updated remain key in maintaining device integrity.
Conclusion
macOS combines multiple security layers, from Gatekeeper’s app verification to XProtect’s malware detection, to provide a well-rounded protection strategy. By understanding and enabling these features, users can enhance their macOS experience without sacrificing security. Whether you are an advanced user or just getting started, these settings and practices will help keep your data safe from potential threats.








